Directord
An asynchronous deployment and operations platform with the aim to better enable simplicity, faster time to delivery, and consistency.
This project is maintained by oshied
Messaging Drivers
Directord is powered by message platforms. As such, to run Directord a messaging driver needs to be selected, which may require additional setup based on the operating environment.
ZeroMQ
Status: Stable
Used for distributed mesh communication between the server and client nodes. No additional setup is required outside of the initial package installation.
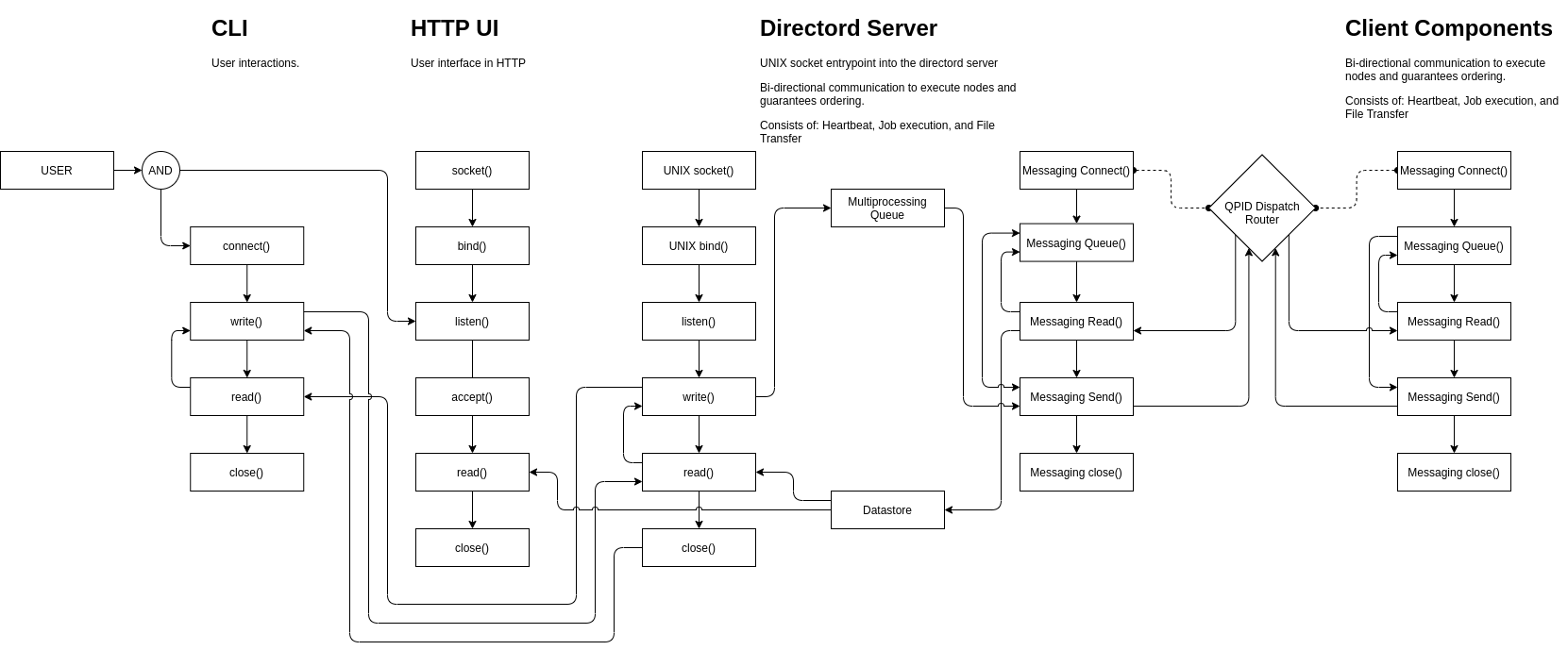
The following diagram shows the application flow when using the ZeroMQ driver.

Directord with the ZeroMQ driver supports two forms of authentication, Shared Key and Curve25519. Both of these authentication methods enhance the security of an environment however both methods have some pros and cons.
| Method | Overview |
|---|---|
| Shared Key | Plain Text |
| Curve25519 | Encryption |
Shared Key Authentication
Shared Key is the easiest method to setup and only requires a shared token be generated on all client and server nodes. Shared Key is only an authentication method and does not provide any encryption. While Shared Key is a simple method to setup, it is not recommended to use this method when dealing with deployments that extend out of a single data center.
Shared Key requires only a simple string to be defined within the Directord configuration file or on the CLI.
Server setup
$ directord --zmq-shared-key ${SECRET_TOKEN} server
Client Setup
$ directord --zmq-shared-key ${SECRET_TOKEN} client
Curve Encryption
Curve25519 is a more complicated method to setup as keys have to be
generated and synchronized to all client and server nodes. While generating
keys is simple with the directord --driver zeromq server --zmq-generate-keys command,
the Curve25519 method is called out as more complex due to the requirement
of file transfers. Curve25519 will encrypt the traffic within the cluster
making it suitable for deployments that extend beyond a single data center.
When starting Directord, both on the server and client, if a keys are directed and no other authentication method is provided Curve25519 will be enabled automatically.
Example key generation, and synchronization to client nodes.
The following command will generate the encryption keys required to enable Curve25519.
$ directord --driver zeromq server --zmq-generate-keys
If the
--zmq-generate-keyscommand is run more than once it will backup old key files before creating new ones. This is important for rollback capabilities should that be needed.
This example shows what needs to be created on remote (client) nodes and which files need to be synchronized to client hosts.
$ ssh root@${REMOTE_NODE} "mkdir -p /etc/directord/private_keys /etc/directord/public_keys"
$ rsync -avz /etc/directord/private_keys/client.key_secret root@${REMOTE_NODE}:/etc/directord/private_keys/
$ rsync -avz /etc/directord/public_keys/*.key root@${REMOTE_NODE}:/etc/directord/public_keys/
Once the keys are all in place the server can be started using the following command.
$ directord --zmq-curve-encryption server
It is also possible to upgrade an existing, un-encrypted, deployment to an
encrypted one using the provided orchestration file, sync-curve-keys.yaml.
This orchestration file assumes keys have been generated on the server.
$ directord orchestrate sync-curve-keys.yaml
This orchestration file will push key files to all nodes within the cluster. This can be restricted by setting targets within the orchestration file or defining a restriction on the CLI. Once files are synchronized the client will need to be configured and restarted.
Curve Key Rotation
When encryption is enabled it is important to be able to rotate keys and restart services whenever required. Directord makes this simple using both its built in functions and via a bootstrap catalog.
To rotate encryption keys natively the following execution commands can be run, which will first generate new keys on the server and run a simple orchestration to rotate the keys across an active cluster.
$ directord --driver zeromq server --zmq-generate-keys
$ directord orchestrate key-rotation.yaml
After key rotation you can validate that all nodes are checking into the cluster using a simple check
$ directord manage --list-nodes
Learn more about Orchestrations here.
Messaging
Status: Stable
Based on OSLO messaging and can make use of many messaging backends. For the purpose of this example, the environment will be configured to use the QPID dispatch router.
The following diagram shows the application flow when using the Messaging driver.
Configuration
With the Directord needs to be configured to run with the messaging driver.
To do this configuration edit the /etc/directord/config.yaml file and add
the following options.
driver: messaging
zmq_server_address: 127.0.0.1
NOTE: The server address is the location of the AMQP Server and can be anywhere, so long as Directord and the client targets are able to router to the defined location.
Requirements
Before running the messaging driver, qdrouterd needs to be setup within the
environment.
Running a local QPID Dispatch Router
$ sudo dnf install qpid-dispatch-router
Once the dependecies are installed, enable and start the server process.
$ sudo systemctl enable qdrouterd.service
$ sudo systemctl start qdrouterd.service
Encryption with SSL
Encryption with SSL can be used to encrypt messages when using the messaging
driver.
Automatic configuration with bootstrap
A script is included with Directord at
tools/scripts/messaging/messaging-ssl-setup.sh that can be used to
automatically configure SSL. The script is used if the
tools/directord-dev-bootstrap-messaging-catalog.yaml bootstrap catalog is
used.
The script uses certmonger and the locally configured CA on the Directord
server to issue certificates. The script is for development use only and not
intended for production.
Manual configuration
SSL configured can be configured manually with the following steps.
-
Configure a CA
Obtain a CA certifcate and key that can be used to sign other certificates needed by Directord. Configure the path to the CA with the
--messaging-ssl-caargument or configuration file option. -
Configure Directord certificate and key
Generate a certificate and private key pair for the Directord server and sign it with the configured CA. The Subject CN of the certificate should match the hostname of the server, or the value of the
--zmq-server-addressconfiguration used by the clients to connect to the server.Specify the path to the server certificate and key with the
--messaging-ssl-certand--messaging-ssl-keyarguments or configuration file options when starting the Directord server. -
Configure Directord client certificates and keys
Generate a certificate and private key pair for each Directord client and sign them with the configured CA. The Subject CN should match the client hostname.
Copy the client certificate and key to each respective Directord client and specify the path to them with the
--messaging-ssl-certand--messaging-ssl-keyarguments or configuration file options when starting the Directord client. -
Configure qdrouterd for SSL
Generate a certificate and private key pair for use with qdrouterd. The Subject CN should match that of the host running qdrouterd. Sign the certificate with the CA.
Configure
/etc/qpid-dispatch/qdrouterd.conffor SSL. See qdrouterd configuration for complete details on configuring qdrouterd. AnsslProfilesection needs to be configured, and thesslProfileattribute in thelistenersection needs to reference thesslProfilesection.An example, which uses the default values for Directord is shown below:
sslProfile { name: my-ssl caCertFile: /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/cm-local-ca.pem certFile: /etc/qpid-dispatch/qdrouterd.conf privateKeyFile: /etc/qpid-dispatch/qdrouterd.conf } listener { sslProfile: my-ssl host: 0.0.0.0 port: 20102 authenticatePeer: false requireSSL: true saslMechanisms: ANONYMOUS }
GRPC
Status: Default
A gRPC server is used to handle message queues between the server and client nodes. No additional service setup is required outside of the initial package installation as the server is managed within Directord. Optional configuration for TLS and authentication may be required for certificate generation.
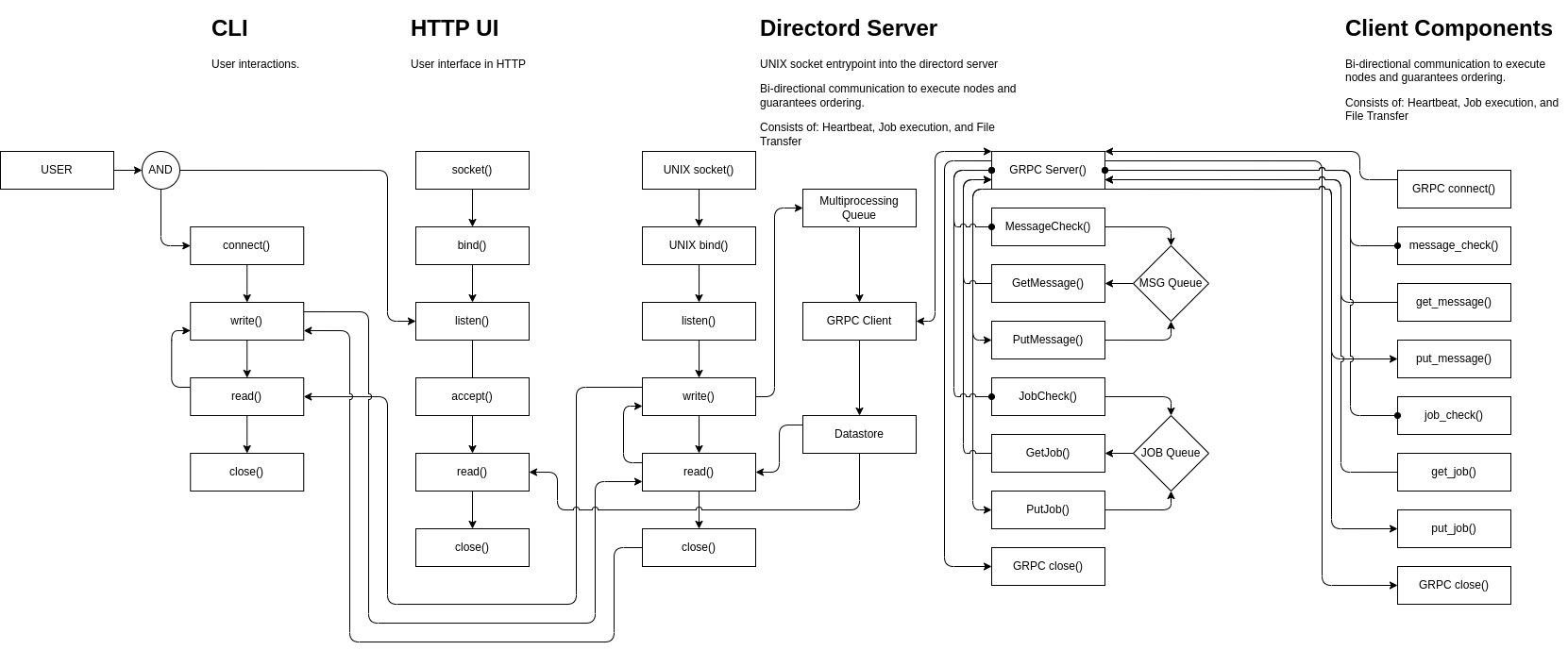
The following diagram shows the application flow when using the GRPCD driver.
Configuration
With the Directord needs to be configured to run with the grpcd driver.
To do this configuration edit the /etc/directord/config.yaml file and add
the following options.
driver: grpcd
grpc_server_address: 127.0.0.1
This configuration enables the grpc server to listen on 0.0.0.0 and connect
to 127.0.0.1. External clients will need to have grpc_server_address
configured to use the server’s IP address or hostname.
Additional options
Additional configuration options are available with the grpcd driver.
--grpc-port(grpc_port) INTEGER gRPC server port. Default: 5558--grpc-server-address(grpc_server_address) STRING gRPC Domain or IP address of the server to connect to. Default: 127.0.0.1--grpc-disable-compression(grpc_disable_compression) BOOLEAN Disable compression between client and server. Default: False--grpc-bind-address(grpc_bind_address) STRING IP address to bind to when starting up the server. Default: 0.0.0.0--grpc-server-workers(grpc_server_workers) INTEGER Number of gRPC server workers. Default: 4--grpc-ssl(grpc_ssl) BOOLEAN Enable gRPC server TLS encruption. Default: False--grpc-ssl-ca(grpc_ssl_ca) STRING gRPC driver SSL CA file path. Default: /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/cm-local-ca.pem--grpc-ssl-cert(grpc_ssl_cert) STRING gRPC driver SSL certificate path. This file on the server is used as the server SSL certificate. On the client it is used for authentication when SSL Client Authentication is enabled. Default: /etc/directord/grpc/ssl/directord.crt--grpc-ssl-key(grpc_ssl_key) STRING gRPC driver SSL certificate key path. This file on the server is used as the server SSL certificate key. On the client it is used for authentication when SSL Client Authentication is enabled. Default: /etc/directord/grpc/ssl/directord.key--grpc-ssl-client-auth(grpc_ssl_client_auth) BOOLEAN Require SSL Client Authenticaiton. If this is enabled,grpc_ssl_certandgrpc_ssl_keyare required on the clients. Default: False
Encryption with TLS
Encryption with TLS can be used to encrypt messages when using the grpcd driver.
SSL Client Authentication
Authentication using client side SSL certificates can be used with the grpcd
driver. When grpc_ssl_client_auth is set to True on the server, clients
must be configured with grpc_ssl_cert and grpc_ssl_key to be able to connect
to the server. If grpc_ssl is set to True and grpc_ssl_client_aith is set
to False on the server, clients only need to have the grpc_ssl_ca configured.
Automatic configuration with bootstrap
Similar to the messaging driver, bootstrap scripts have been created to aide
in generation of SSL CA and certificate generation. A script is included with
Directord at tools/scripts/grpcd/grpcd-ssl-setup.sh that can be used to
automatically configure SSL. The script is used if the
tools/directord-dev-bootstrap-grpc-ssl.yaml bootstrap catalog is used.
The script uses openssl to generate a local CA and certificates for
encryption and authentication.
Manual Configuration
-
Configure a CA
Obtain a CA certifcate and key that can be used to sign other certificates needed by Directord. A CA is necessary to sign certificates to use fori client authentication. If client authentication will not be used but TLS is used to encrypt the trafic, only the certificate is required.
-
Configure Directord server certificate and key.
Generate a certificate (or cetificate request) and key pair for the Directord server. If using self signed CA, sign the certificate with the CA. The Subject CN of the certificate should match the hostname of the server or the value of
--grpc-server-address(grpc_server_addres).Specific the path to the server certificate and key with the
--grpc-ssl-cert(grpc_ssl_cert) and--grpc-ssl-key(grpc_ssl_key) arguments or configuration file options when starting the Directord server. -
Configure Directord client CA, certificate, and key.
On the client use
--grpc-ssl(grpc_ssl) to enable ssl. The CA option--grpc-ssl-ca(grpc_ssl_ca) should be configured with the path to the CA certificate.If SSL Client Authentication is enabled, the
--grpc-ssl-cert(grpc_ssl_cert) and--grpc-ssl-key(grpc_ssl_key) must be configured for the client to be able to connect to the server. If SSL Client Authentication is not enabled, the options can be skipped.